给定 $n$ 个整数 $\langle a_1, a_2 … a_n \rangle$,在 $[0; 2^m)$ 的范围内。对于 $k \in [0; m]$,求选出一个子集使得异或和的二进制表示有 $k$ 个 $1$ 的方案数。
$1 \leq n \leq 2 \times 10^5,\ 0 \leq m \leq 53$。
0x01
定义:
- $\operatorname{popcount}(x)$ 表示 $x$ 的二进制表示下 $1$ 的个数
- $\langle i, j \rangle = \operatorname{popcount(i\ \&\ j)}$
对于线性基 $S$,定义:
- $\operatorname{span}(S)$ 表示 $S$ 张成的向量空间
- $F(S) = \sum_{x \in \operatorname{span}(S)} z^x$
- $P(S) = \sum_{x \in \operatorname{span}(S)} z^{\operatorname{popcount}(x)}$
对于此题,定义
首先你已经会了一个 $O(2^{\operatorname{rank}(A)})$ 的暴力,下文我们介绍一种 $O(2^{m-\operatorname{rank}(A)})$ 的算法,就可以通过分治在 $O(2^{m/2})$ 的时间复杂度内通过本题。
0x02
由线性基的基本性质,可以得到:
在此基础上枚举 $x \in \operatorname{span}(A)$ 有
由于是按位相乘,考虑方程 $x^2=x+1$ 的实根仅有
故 $[z^i] \operatorname{FWT}(F(A)) \in \{0, 2^{\operatorname{rank}(A)}\}$。
0x03
让我们再回到 $\operatorname{FWT}$ 运算本身的意义:
如果存在 $x$ 使得 $(-1)^{\langle i,x \rangle} = -1$,则 $\operatorname{FWT}(A)_i$ 只能为 $0$。
$\langle x,y \rangle$ 和 $\oplus$ 运算满足结合律:
可以通过把 $\&$ 理解为二进制按位乘法,$\oplus$ 理解为二进制不进位加法来证明。
故我们只需检验 $A$ 中的每个基底而非 $\operatorname{span}(A)$ 即可判断这一位的值。
0x04
定义 $A$ 的正交线性基为 $B$,使得对于所有 $x \in \operatorname{span}(A), y \in \operatorname{span}(B)$,满足 $\operatorname{popcount(x \& y)}$ 是偶数,且 $\operatorname{rank}(A) + \operatorname{rank}(B) = m$。
根据前面的引理,有
一种简单的正交线性基构造方式是
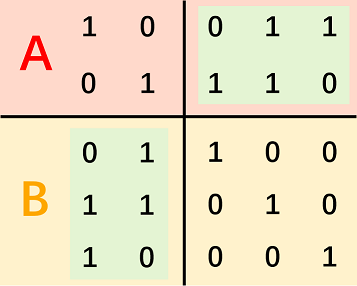
用高斯消元整理关键位,旋转右上角到左下角得到。
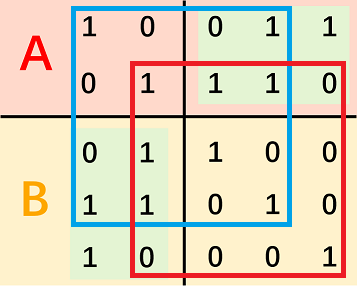
证明可以考虑图中圈出矩形的左上角和右上角一定为 $1$,而两向量的异或的 $\operatorname{popcount}$ 为偶数,那么左下角和右上角的数要么全为 $0$,要么全为 $1$。
0x05
知道了正交线性基怎么求,如何计算答案呢?
考虑用 $\operatorname{FWT}$ 表示答案统计:
其中 $G^c$ 表示 $\sum_{x \geq 0} z^x [\operatorname{popcount}(x)=c]$。
其中:
由于 $\operatorname{FWT}(F(A)) = F(B) \cdot 2^k$,而 $B$ 中的元素只有 $2^{\operatorname{rank}(B)} = 2^{m - \operatorname{rank}(A)}$ 个。故通过暴力得到 $P(B)$,即可通过组合数计算得 $P(A)$。
0x06
代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
| #include<bits/stdc++.h>
template<class T> inline void read(T &x){
x=0; register char c=getchar(); register bool f=0;
while(!isdigit(c))f^=c=='-',c=getchar();
while(isdigit(c))x=x*10+c-'0',c=getchar(); if(f)x=-x;
}
const int N=60,mod=998244353;
int n,m,k,t,c[N];
long long f[N],g[N];
struct z {
int x;
z(int x=0):x(x){}
friend inline z operator*(z a,z b){return (long long)a.x*b.x%mod;}
friend inline z operator-(z a,z b){return (a.x-=b.x)<0?a.x+mod:a.x;}
friend inline z operator+(z a,z b){return (a.x+=b.x)>=mod?a.x-mod:a.x;}
}p[N],q[N],fac[N],ifac[N];
inline z C(int n,int m){return n<m?0:fac[n]*ifac[m]*ifac[n-m];}
inline z fpow(z a,int b){z s=1;for(;b;b>>=1,a=a*a)if(b&1)s=s*a;return s;}
inline void insert(long long x){for(int i=m-1;i>=0;i--)if((x>>i)&1){if(f[i])x^=f[i]; else {f[i]=x; return;}}}
int main(){
read(n),read(m);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){long long x; read(x),insert(x);}
for(int i=0;i<m;i++)for(int j=i+1;j<m;j++)if((f[j]>>i)&1)f[j]^=f[i];
for(int i=0;i<m;i++)if(f[i])c[i]=k++;
for(int i=0;i<m;i++)if(!f[i])c[i]=k+(t++);
for(int i=0;i<m;i++)if(f[i])for(int j=0;j<m;j++)if((f[i]>>j)&1)g[c[i]]|=1ll<<c[j];
for(int i=0;i<k;i++)for(int j=k;j<m;j++)if((g[i]>>j)&1)g[j]|=1ll<<i;
for(int i=k;i<m;i++)g[i]|=1ll<<i;
if(k<=((m+1)>>1)){
std::function<void(int,long long)> dfs=[&](int i,long long s){
if(i>=k){p[__builtin_popcountll(s)].x++;return;}
dfs(i+1,s),dfs(i+1,s^g[i]);
};
dfs(0,0ll);
}else{
std::function<void(int,long long)> dfs=[&](int i,long long s){
if(i>=m){q[__builtin_popcountll(s)].x++;return;}
dfs(i+1,s),dfs(i+1,s^g[i]);
};
dfs(k,0ll);
fac[0]=ifac[0]=ifac[1]=1;
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++)fac[i]=fac[i-1]*i;
for(int i=2;i<=m;i++)ifac[i]=(mod-mod/i)*ifac[mod%i];
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++)ifac[i]=ifac[i-1]*ifac[i];
for(int c=0;c<=m;c++)for(int d=0;d<=m;d++)for(int i=0;i<=c;i++){
p[c]=p[c]+fpow(2,mod-1+k-m)*q[d]*(i&1?mod-1:1)*C(d,i)*C(m-d,c-i);
}
}
for(int i=0;i<=m;i++)printf("%d%c",(p[i]*fpow(2,n-k)).x," \n"[i==m]);
}
|